Anatomy of the Great Financial Crisis ...
After completing this reading, you should be able to: Describe the historical background... Read More
After completing this reading, you should be able to:
Companies should address each of their significant risks and the interdependence of risks. Since risks are highly dynamic and correlated with each other, an integrated approach is required to manage them. Suboptimal performance may result from a fragmented approach towards risk management in which risk is managed in organizational silos. If the interdependence of risks like credit risk, market risk, operational risk, etc. is not captured in the risk management activities, the attempts to address risks are bound to remain inefficient and faulty.
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is responsible for organizing and coordinating an integrated risk management framework for the firm. It establishes policies and directives for managing risks across business units and provides the senior management with overall control and monitoring of the organization’s exposure to significant risks. Since individual risk functions have different measures and methodologies of measuring and reporting risks, the management may not have a clear picture of the firm’s total risk exposure. Top management should have information about the indicators of risk, the priority with which the risks are to be addressed, actual losses in the past, and their assessment and regulatory requirements as well as corporate risk policies. ERM is effective in providing the management with a firm-wide picture of risks that the business units face.
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) defined ERM in 2004 as follows:
“ERM is a process, effected by an entity’s board of directors, management and other personnel applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives.”
ERM approach to risk management and the presence of the chief risk officer in a firm enable the integration of risk management activities across business units and allow efficient management of risk interdependencies. Since almost all firms have finance, audit, and compliance functions, ERM function enables them to function cohesively.
In the silo approach to risk management, each business unit has its own measure of risk and methodology of reporting risk. These reports may not represent the overall organization risk and may be contradictory. Since the Board of Directors needs to address the risks as per their importance so that the overall business conforms to the risk appetite, it needs to have an organization level perspective of the risks and their impacts on the turnover. ERM function can provide the Board with such details and can bring to the notice of the Board policy exceptions, risk limit breaches and priority of individual business risks.
An integrated top-down approach to risk management furnished by ERM function provides directives for rationalizing key business decisions like resource allocation, competitive pricing, product differentiation, etc. A portfolio view of all risks leads to an adequate handling of risk interdependencies and an efficient risk hedging as well as risk transfer. ERM function enables companies to make risk-adjusted decisions based on company-wide risk exposures and strategies to mitigate or handle them. This, in turn, improves the performance and efficiency of the company.
The Board of Directors, regulators, and auditors are concerned with an organization’s methods of risk management and the effectiveness of such methods. Further, the availability of a wide range of risk transfer products like credit derivatives, etc., direct pressure from rating agencies and stakeholders, and availability of measures like VaR ( value at risk ) that can be used in almost all business units, have made it less acceptable to manage risk in obsolete ways.
Chief Risk Officer reports directly to the Board of Directors about the overall risk exposure of the firm and methods to handle it. CRO is the leader of the ERM function in a firm. The CRO supervises the organization’s risk management framework and lays down policies and directives for integrating business units’ risks into a portfolio structure. Risk indicators are devised by the CRO to present an overall report of business risk and key exposures to the Board of Directors. The CRO is also responsible for resource and capital allocation based on the firm’s priorities and risk-adjusted returns possibilities from investments. The CRO reports the firm’s key risk exposures, the methodology of risk management, and the firm’s long-term financial health prospects to the stakeholders like the Board of Directors, regulators, etc.
To keep the CRO effective in conducting his duties, an organization should provide for the CRO direct reporting access to the Board of Directors. The presence of the CRO and a dedicated risk management function have increased the efficiency with which organizations tackle their risk exposures. The option to let the CEO or the CFO do the CRO’s tasks may lead to detrimental consequences for the firm’s long-term economic help because the function of a CEO to improve business profits may lead to him undermining the risk associated with the returns.
The necessary skills and qualities that a CRO should have are as follows:
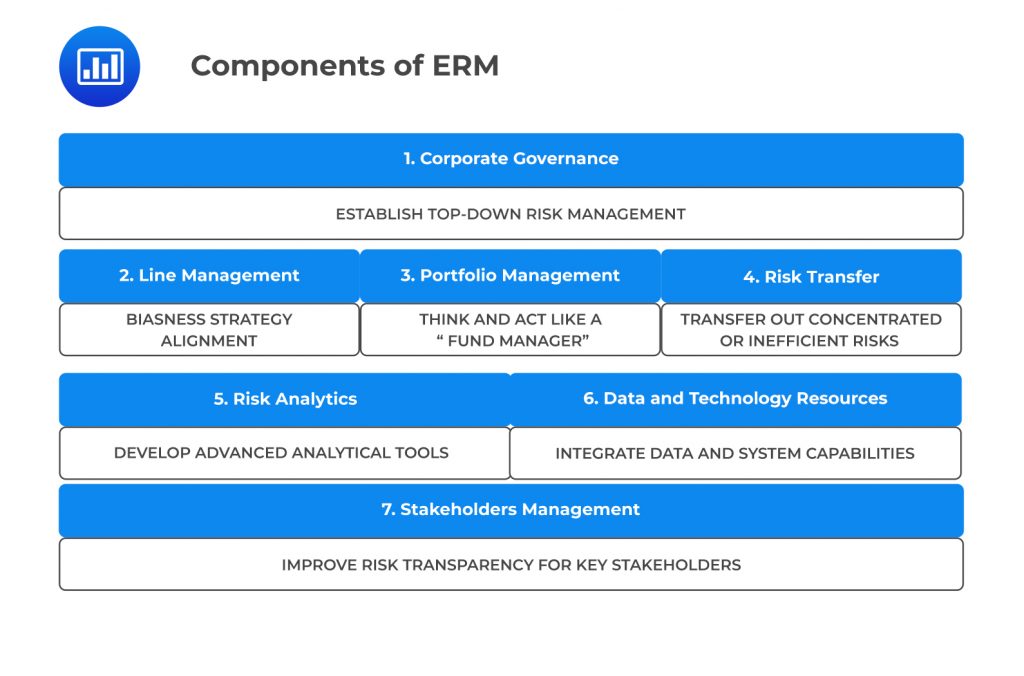 Corporate Governance
Corporate GovernanceAppropriate organizational processes, policies, and directives related to measurement and management of risk should be laid down by the Board of Directors and the management of the firm. Regulatory requirements and penalties associated with non-compliance force the hands of management to take risk management very seriously. From the viewpoint of enterprise risk management, the Board of directors should:
Line management should consider the corporate risk policy while taking business decisions and should steer business strategies in the direction most suitable for increasing risk-adjusted returns. Risks related to business lines should be priced into products and services. Business decisions should be taken after accounting for expected losses, opportunity costs, long term profitability, and required expertise as well as resources to align risks with corporate risk policies. Audit and review functions should do due diligence. Risk-adjusted returns and pricing should be taken into consideration for assessing growth opportunities.
The risk management function should not assess and handle the risks of business units individually. Rather, for ensuring internal diversification and for optimizing overall company returns, individual units should be considered together as parts of a portfolio and specific risks and return limits should be set for them. The integration of risk management function can help in the creation of natural hedges within the company, thus reducing transaction costs. Thus, ERM function associates the shareholder value creation process with risk management.
Financial instruments like options, futures, and insurances can be used to reduce and transfer risks that are undesirable for a firm. A portfolio view of risks helps to assess the combination of financial products that provide the most cost-effective solution to the risk reduction and transfer problem. Integrated risk management also helps to use natural hedging strategies that exist in the risk portfolio. For example, a firm may hedge part of its currency risks by matching payables with receivables within the firm. Firms should structure its business policy to reduce the accumulation of high amounts of risk in certain areas where risk-adjusted returns are not promising.
Advanced technology and risk management techniques can be used to calculate the cost of risk reduction and transfer through financial products. Risk management strategies should be based on comparative advantage and risks should be transferred only if the cost involved is not more than the cost incurred by holding it. Thus, risk analytics provides methods to assess cost-effectiveness in hedging and transferring risk as well as increasing risk-adjusted returns, risk-adjusted net present value, etc.
Data from underlying businesses and the market should be aggregated to make a fair assessment of business line and risk management functions associated with them. ERM should ensure this aggregation and should also lay down principles and strict guidelines to preserve and improve the quality of data fed into risk management systems. An organization should have a good quality of software and technological assets to be used by the risk management function.
Since the ultimate goal of a firm should be stakeholder’s value maximization, appropriate risk management policies should be in effect that make the entire process transparent to the stakeholders. The Board of Directors should have periodic reports about the risk exposures of the firm while the regulators should be assured that the firm is complying with all industry standards. Communication of risk management methods, along with the assurance of their integrity and appropriateness, is essential for a firm’s healthy continuation of business.
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.