Characteristics of Representative Indu ...
[vsw id=”labqtlwTF_c” source=”youtube” width=”611″ height=”344″ autoplay=”no”] A valuable comparison may include the following... Read More
Determining which industries will earn economic profits (return on invested capital in excess of the cost of capital) is typically dependent on understanding the competitive environment within the industry. Thus, strategic analysis is the competitive environment analysis, emphasizing the implications of the environment for corporate strategy. Michael Porter’s “five forces” framework is the classic starting point for strategic analysis.
Porter identified five determinants of competition intensity in an industry
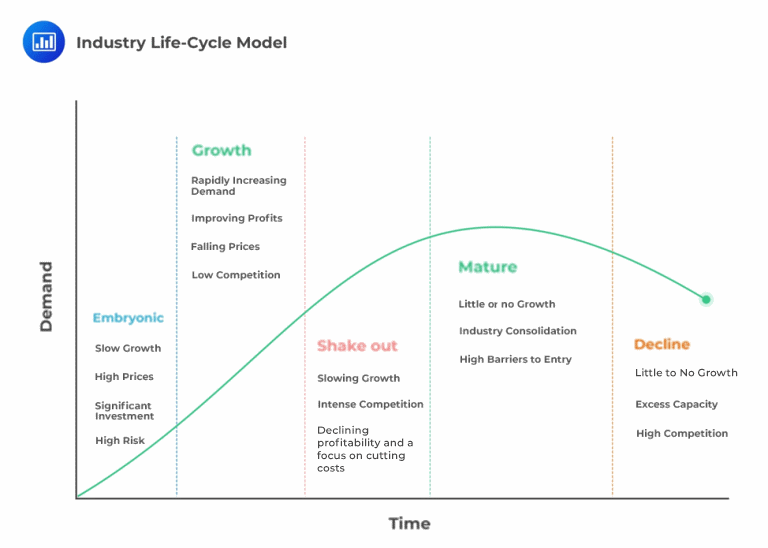
An industry’s life-cycle position often has a large impact on its competitive dynamics, making this position an important component of the strategic analysis of an industry. There are five stages in the industry life-cycle model: embryonic, growth, shakeout, mature, and decline. Each stage is characterized by different opportunities and threats, as we will see in a future learning objective.
Question
In which industry life cycle stage is there focus on cutting costs because the competition is intensifying?
- Mature stage.
- Decline stage.
- Shakeout stage.
Solution
The correct answer is C.
The maturity phase begins with a shakeout period, during which growth slows and focus shifts toward expense reduction. Shakeout usually refers to the consolidation of an industry where some businesses are naturally eliminated because they are unable to grow along with the industry.
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.