Business Cycles and Short-and Long-ter ...
The business cycle refers to variations of economic productivity–often measured in terms of... Read More
The shape of the yield curve is often cited as a leading reliable economic indicator. The yield curve maps the relationship between interest rates and the maturity of fixed-income investments on a graph. On the horizontal axis is time or maturity, while on the vertical axis are rates that are prevalent in the economy.
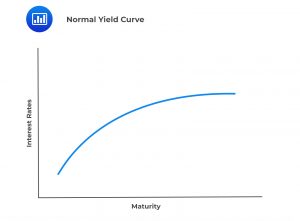
The yield curve tends to be steep at the bottom of the cycle, flatten during the expansion until it is very flat or even inverted at the peak, and re-steepen during the subsequent contraction.
A flattening or inverted yield curve involves downward pressure on long-term rates and upward pressure on short-term rates. With longer-term loans comes more risk to the lender, so an inverted curve is not a logical way for the markets to operate long-term and is thus typically thought of as a harbinger of unsettling times ahead.
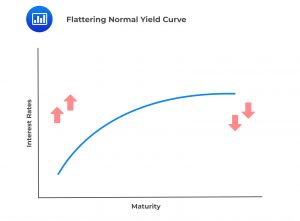
Bottom of the cycle + Expansion: Steepening yield curve.
At the top of the peak: Flattened or inverted yield curve.
Top of peak + Contraction: Steepening of the yield curve.
Question
Which of the following would most likely be interpreted as a sign of economic improvement on the horizon?
- A flattening yield curve.
- An inverted yield curve.
- A steepening yield curve.
Solution
The correct answer is C.
A steepening curve leaves its flatter or inverted form and moves towards a normal and healthy shape, indicating a longer-term expansionary cycle.
A is incorrect. A flattening of the yield curve denotes an economy moving from a standard yield curve toward an inverted yield curve. While this could signal that the economy is still in an expansionary mode, it is more likely that whatever expansion is left will be short-lived as an inverted yield curve is on the horizon.
B is incorrect. An inverted yield curve is known as a predictor of a recession, not an expansion.
Asset Allocation: Learning Module 1: Capital Market Expectations – Part 1 Framework and Macro Considerations; Los 1(i) Interpret the shape of the yield curve as an economic predictor and discuss the relationship between the yield curve and fiscal and monetary policy
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.