Factors
After completing this reading, you should be able to: Describe the process of... Read More
After completing this reading, you should be able to:
There are three broad categories of deposits offered by banks and other deposit institutions. These include:
We discuss them in the following sections:
A transaction deposit is an account used primarily to make payments for purchases of goods and services. The financial-service providers must instantly honor whatever withdrawals a customer makes in person, or by a third party chosen by the customer to be the recipient of funds withdrawn.
Transaction deposits are further divided into noninterest-bearing transaction deposits and interest-bearing transaction deposits.
Savings or thrift deposits have features that attract funds from customers who wish to reserve money in expectation of future expenditures or for financial emergencies. In other words, a thrift account is an account whose primary purpose is to encourage the bank customer to save rather than make payments. Compared to transaction deposits, non-transaction deposits usually pay substantially higher interest rates and are less costly to process and manage for the offering institutions.
Non-transaction deposits are split into:
Retirement savings deposits can be categorized into three:
The main difference between Roth IRAs and traditional IRAs is that Roth IRAs are financed with after-tax dollars. This means that the contributions are not liable to tax-deductions, but once one starts withdrawing funds, the money is tax-free. Conversely, traditional IRA deposits are made with pre-tax dollars. This implies that an individual is liable to a tax deduction on their contribution and consequently pays income tax when they take out money from the account when they retire.
Interest rates on deposits majorly depend on:
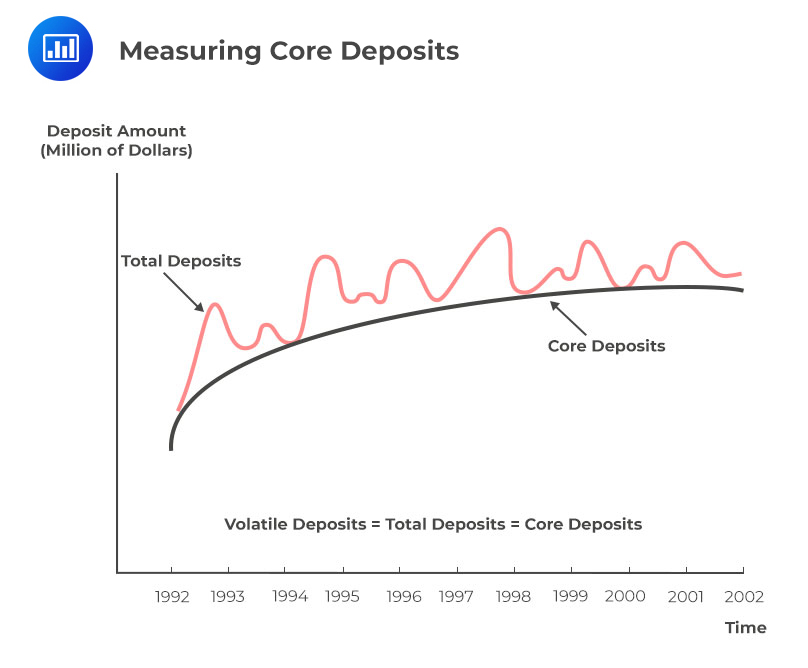
Core deposits are a stable base of funds that are not highly sensitive to market interest rate fluctuations and which tend to remain with the bank. The following figure illustrates the core deposits.
 Methods Used to Determine the Pricing of Deposits and Calculation of the Price of a Deposit Account
Methods Used to Determine the Pricing of Deposits and Calculation of the Price of a Deposit AccountThe main goal of depository institutions is to price their deposit services in a way that attracts new funds and makes a profit. The management faces a difficult decision-making scenario as it has to balance between the institution’s needs to pay a high enough interest return to attract and hold customer funds, at the same time, avoid paying an interest rate so costly it erodes any potential profit margin.
However, financial institutions are price takers, not price makers in a perfectly competitive market. The management must, therefore, decide if it wishes to attract more deposits and hold all those it currently has by offering depositors at least the market-determined price, or whether it is willing to lose funds.
Methods of calculating the price of a deposit account are discussed below:
Cost-plus deposit pricing encourages banks to determine the costs they incur in labor and management time, materials, among others, in offering each deposit service. Cost-plus pricing typically calls for a bank to charge deposit service fees enough to cover all the costs of providing the service in addition to a small margin for profit.
Every deposit service may be priced high enough to recover all or most of the cost of offering that service, using the following cost-plus pricing formula:
$$ \begin{align*} & \text{Unit price charged the customer for each deposit service} \\ & =\text{(Operating expense per unit of deposit service} \\ & + \text{Estimated overhead expense allocated to the deposit service function} \\ & + \text{Planned profit margin from each service unit sold)} \\ \end{align*} $$
The above equation ties deposit pricing to the cost of deposit-service production, which has encouraged deposit providers to keenly match prices and expenses and eradicate many formerly free services.
Nowadays, most depository institutions charge for excessive withdrawals, customer balance inquiries, bounced checks, and ATM usages, as well as raising required minimum deposit balances, among others. These trends have been favorable to depository institutions.
ABC savings bank determines that its basic checking account costs the bank $3.00 per month in servicing costs (assume the servicing costs are labor and computer time) and $2.00 per month in overhead expenses. This account requires a $600 minimum balance. Additionally, the bank also tries to build a $0.60 per month profit margin on these accounts.
Determine the monthly fee that the bank should charge each customer.
Breaking down the information given in the question.
Operating expense per unit of deposit service = $3.00
Estimated overhead expense allocated to the deposit service function = $2.00
Planned profit margin = $0.60
Following the cost-plus profit pricing formula, the monthly fee is:
$$ \text{Monthly fee} = $3.00 + $2.00 + 0.60 = $5.60 \text{ per month} $$
ABC savings bank determines that its basic checking account costs the bank $3.00 per month in servicing costs (assume the servicing costs are labor and computer time) and $2.00 per month in overhead expenses. This account requires a $600 minimum balance. Additionally, the bank also tries to build a $0.60 per month profit margin on these accounts.
Analysis of ABC Savings Bank Customer accounts reveals that for each $150 above the $600 minimum balance maintained in its checking accounts, the bank saves about 5% in operating expenses with each customer account.
For a customer who is consistent in maintaining an average monthly balance of $1,200, how much should the bank charge to protect its profit margin?
If the bank saves about 5% in operating expenses for each $150 held in balances above the minimum of $600, then a customer who maintains an average monthly balance of $1,200 saves the bank 20% in operating expenses.
$$ \text{New operating expenses} = $3.00 – (20\%×$3.00)=$2.40 $$
The appropriate amount that the bank should charge to protect its profit margin is therefore
$$ \text{Monthly fee} = $2.40 + $2.00 + $0.60 = $5.00 \text{ per month} $$
Many financial analysts would argue that the marginal cost, and not the historical average cost, should be used to price deposits and funding sources. This is because frequent fluctuations in interest rates make historical average cost an unreliable standard for pricing.
The marginal cost formula is as follows:
$$ \begin{align*} \text{Marginal cost} & = \text{Change in total cost} \\ & =\text{New interest rates}×\text{Total funds raised at new rate} \\ & – \text{Old interest rate× Total funds raised at old rate} \\ \end{align*} $$
Where,
$$ \text{Marginal cost rate} =\cfrac {\text{Change in total cost}}{\text{Additional funds raised}} $$
A bank that has a base amount of savings deposits of $50 million and currently pays 8% rate on these funds. The bank seeks to raise additional funds but will have to increase the interest rate as the amount of cash raised increases. Management anticipates an investment yield of 10% after investing deposits.
$$ \small{\begin{array}{l|c|c|c|c|c|c|c} \bf{\text{Funds} \\ \text{Raised}} & \bf{\text{Average} \\ \text{Rate} \\ \text{Paid} } & \bf{\text{Total} \\ \text{Interest} } & \bf{\text{Marginal} \\ \text{Cost} } & \bf{\text{Change in} \\ \text{Total} \\ \text{Cost} } & \bf{\text{Expected} \\ \text{Revenue} } & \bf{\text{Difference} \\ \text{Expected} \\ \text{less} \\ \text{Marginal} } & \bf{\text{Total} \\ \text{Additional} \\ \text{Profit} } \\ \hline {50m} & {8.0\%} & {4m} & {4m} & {8.0\%} & {10.0\%} & {2.0\%} & {\$1m} \\ \hline {100m} & {8.5\%} & {8.5m} & {4.5m} & {9.0\%} & {10.0\%} & {1.0\%} & {\$1.5m} \\ \hline {200m} & {9.0\%} & {18m} & {9.5m} & {9.5\%} & {10.0\%} & {0.5\%} & {\$2m} \\ \hline {300m} & {9.5\%} & {28.5m} & {10.5} & {10.5\%} & {10.0\%} & {-0.5\%} & {\$1.5m} \\ \hline \end{array}}$$
The calculations are as follows:
$$ \begin{align*} \text{Total interest} &= \text{Funds raised}×\text{Average Rate Paid} \\ &=50,000,000×8.0\%= 4,000,000 \\ \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} \text{Marginal cost} & = \text{Change in total cost} \\ & =\text{New interest rates}×\text{Total funds raised at new rate} \\ & – \text{Old interest rate× Total funds raised at old rate} \\ & =(8.5\%×100,000,000)-(8.0\%×50,000000)=4,500,000 \\ \end{align*} $$
For the second case,
$$ \text{Change in Total Cost} =\cfrac {4,500,000}{100,000000-50,000000}=9.0\% $$
The bank will, therefore, make a total additional profit of the amounts given in the last column. Total profit tops out at $200,000,000. It would not pay the bank to go beyond this point. The 9% deposit rate is, therefore, the best choice, given all the assumptions and forecasts made.
At some point, expanding the deposit base becomes unprofitable. At that point, the bank must either find a lower cost of funding (on the margin), or higher-yielding assets.
Depository institutions, particularly banks, use conditional pricing as a tool to attract the kind of depositors they want to have as customers. In this case, a depository institution sets up a schedule of fees in which the customer pays a low fee or no fee given that the deposit balance is above some minimum level. However, the customer is liable to higher charges if the average balance drops below that minimum level. In other words, the customer pays the price conditional on how they use a deposit account.
Conditional pricing is based on one or more of the following factors:
The customer chooses the deposit plan that accrues the lowest fees possible and maximum yield, or both, given the number of checks he or she plans to write, the expected number of deposits and withdrawals he plans to make, and/or the anticipated average balance he plans to keep in his/her account.
Bright Savings bank has posted the following fees schedule for its business checking accounts:
$$ \textbf{Average Monthly Account Balances} $$
$$\small{ \begin{array}{l|c|c} \textbf{Range} & \textbf{Monthly Maintenance Fee} & \textbf{Charge Per Check} \\ \hline {\text{Over } $2,000} & {$0} & {$0} \\ \hline {$1,500 – $2,000} & {$3} & {$0.20} \\ \hline {\text{Less than } $1,500} & {$5} & {$0.30} \\ \end{array}}$$
What is the type of Bright’s business pricing?
Bright Savings Bank has posted a deposit fee schedule that has an allowance of free checking for average account balances of over $2,000. Lower balances can only be assessed at an increasing monthly maintenance fee plus an increased per check charge in line with falling average monthly account balances.
This is conditional pricing designed to encourage large and stable accounts. This would perhaps give the bank more money available for usage and a more stable funding base. The condition of the higher fee on under $1,500 accounts is strict and stiff, and that may chase away small depositors to other banks, which is the goal the financial institution is pursuing.
Depository institution prices deposits according to the number of services purchased or utilized. The depositor may be given lower fees or have a part of the cost waived if they have used two or more services – for example, having a checking account, a savings account, and his/her mortgage at the same financial institution.
Depository institutions can sell deposits at comparatively low rates of interest relative to interest rates provided by other financial instruments since they have government-supplied deposit insurance. The FDIC was established to insure deposits and protect money supply in cases where depository institutions with FDIC membership failed. The FDIC only covers those deposits payable in the United States.
Banks are insured through the Bank Insurance Fund (BIF), while savings and loans are insured through the Savings and Association Insurance Fund (SAIF). Deposits of all types are typically covered up at least $250,000 for each given account holder within the same bank. Note that deposits held in separate institutions are insured separately.
Basic (lifeline) banking is the low-cost deposits and other services designed to meet the banking needs of customers who cannot afford standard bank service offerings. These services carry low service fees and usually do not provide all the components of banking services which carry full-service charges.
The compulsion on managers to offer essential banking services has triggered an extensive controversy. From a profit-making perspective, banks should only provide valuable (profitable) services. On the other hand, the government partially subsidizes financial institutions in the form of low-interest loans and deposit insurance. This obliges them to some public-service responsibilities, which may include providing certain essential services to all liable customers, regardless of their income or social status.
As mentioned in the previous subsection, it is the responsibility of financial institutions that take deposits to provide lifeline financial services. This has been incorporated in the new legal requirements to serve the local community entirely. Furthermore, essential aids may be extended to depository institutions from the government, granting them a competitive advantage over other financial institutions. If depository institutions benefit from protection backed ultimately by the public’s taxes, they have a public responsibility to provide some services that are accessible to all.
Overdraft fees and revenue have skyrocketed over the past decade. However, there is no evidence that banks have been earning profits or “rents” from the growing overdraft protection usage. On the contrary, there is an emerging competitive market for overdraft protection among banks offering overdraft services and with comparable products, such as payday lending. There is no evidence of reasonable returns to the banking industry, generally from the growth of overdraft protection.
The Truth in Savings Act of 1991 requires depository institutions to make greater disclosure of the terms attached to the deposits they sell the public. Specifically, it requires consumers to be informed of the deposit terms before they open a new account.
Under this act, depository institutions must disclose:
The annual percentage yield is calculated using:
$$ \begin{align*} \text{APY earned} &=100 \left[ {\left(1 +\cfrac {\text{Interest earned}}{\text{Average account balance}}\right)}^{\frac {365}{\text{Days in period}} } -1 \right] \end{align*}$$
where the account balance is the average daily balance held in the deposit for the period covered by each account statement. Customers must be informed of the effect of early withdrawals on their expected APY.
James Leo is a customer at ABC Savings Bank Limited. Leo holds a savings deposit in the bank for a year. The balance in the account stood at $3,000 for 200 days and $150 for the remaining days of the year.
Assuming that ABC Bank paid Leo $10.05 in interest earnings for the year, what APY did Leo receive?
The correct formula is:
$$ \begin{align*} \text{APY earned} &=100 \left[ {\left(1 + \cfrac {\text{Interest earned}}{\text{Average account balance}}\right)}^{\frac {365}{\text{Days in period}} } -1 \right] \\ \text{Average account balance} & =\cfrac {($3,000×200 \text{ days})+($150×165 \text{ days})}{365 \text{ days}}=$1,712 \\ \text{APY} & =100\left[ { \left( 1+\frac { $10.05 }{ $1,712 } \right) }^{ \frac { 365 }{ 365 } }-1 \right] =0.59\% \\ \end{align*} $$
Practice Question
Abacca Bank determines that its basic checking account costs the bank $3.00 per month in servicing costs (assume the servicing costs are labor and computer time) and $2.00 per month in overhead expenses. This account requires a $500 minimum balance. Additionally, the bank also tries to build a $0.50 per month profit margin on these accounts.
Further analysis of Abacca Bank customer accounts reveals that for each $100 above the $500 minimum balance maintained in its checking accounts, the bank saves about 6% in operating expenses with each customer account.
For a customer who is consistent in maintaining an average monthly balance of $700, how much should the bank charge to protect its profit margin?
A. $3.14
B. $4.64
C. $2.64
D. $5.14
The correct answer is D.
If the bank saves about 6% in operating expenses for each $100 held in balances above the minimum of $500, then a customer who maintains an average monthly balance of $700 saves the bank 12% in operating expenses.
$$ \text{New operating expenses} = $3.00 – (12\%×$3.00)=$2.64 $$
The appropriate amount that the bank should charge to protect its profit margin is therefore:
$$ $2.64 + $2.00 + $0.50 = $5.14 \text{ per month} $$