Goals-based Approach
A goals-based asset allocation process combines into an overall portfolio numerous sub-portfolios, each... Read More
The business cycle refers to variations of economic productivity–often measured in terms of GDP–around its long-term trend rate. It is this long-term trend rate that serves as an anchor for forecasting business environments. This is because the economy cannot sustainably grow faster than its long-term trend rate and because the long-term trend rate means reverting. Since the movements around the trend rate are ultimately stochastic, the business cycle phases can often vary in intensity and length. Despite these fluctuations, a pattern emerges. The business cycle exhibits stochastic processes because it reflects economic decisions that:
The output gap is the difference between the actual output of an economy and the maximum potential output of an economy expressed as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP).
This formula states that when actual output exceeds maximum output, a positive output gap exists since the economy is outperforming, i.e., overheating. A negative output gap is the opposite, the actual output below the maximum potential output.
Despite varying length and intensity, business cycles tend to follow a pattern. This pattern is encapsulated in the graphic below.
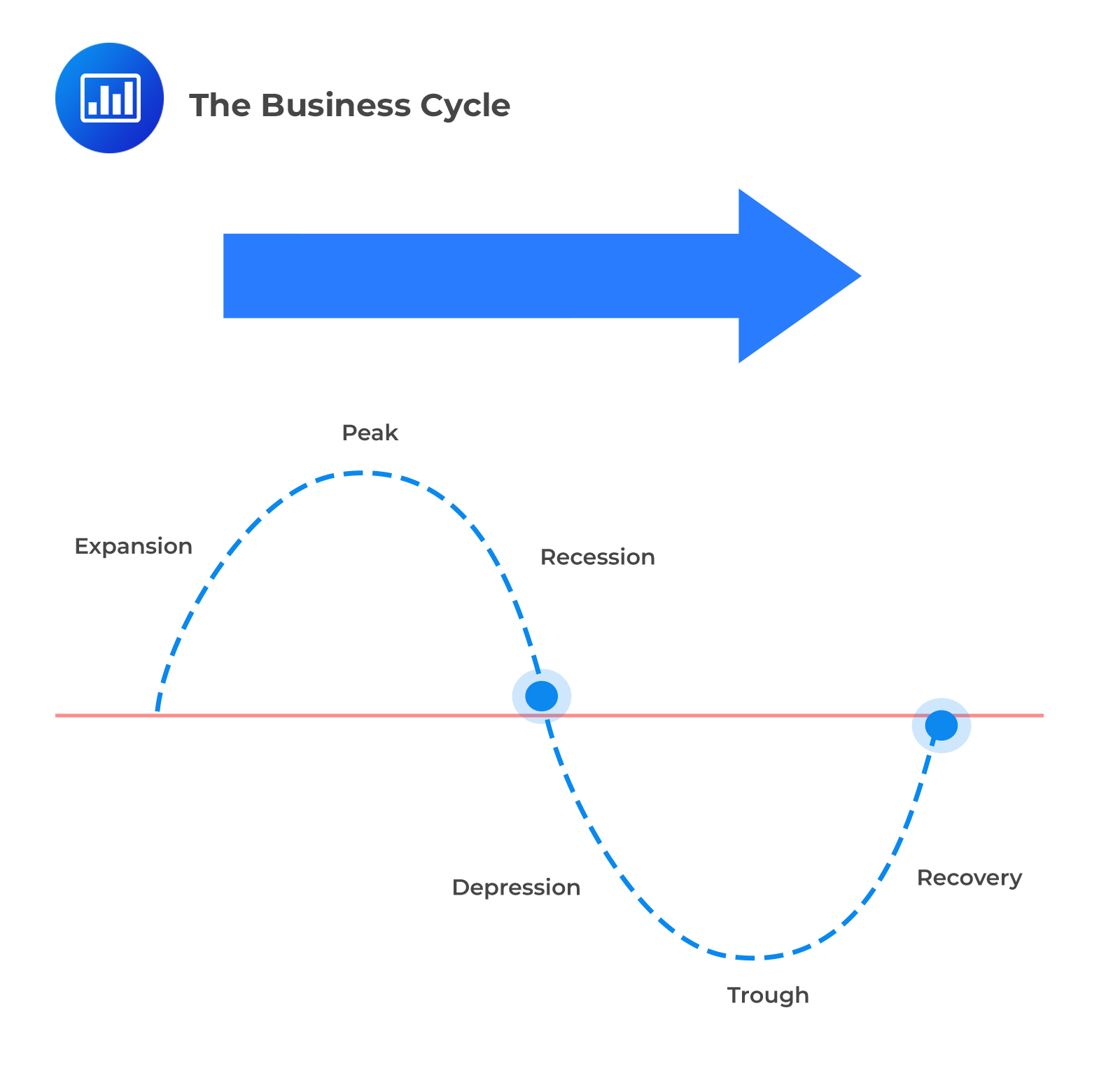
The formulation of capital market expectations seems straightforward under the previous descriptions. If this is true, then making a few forecasts and earning abnormal returns should be easy. The truth is that it is quite a bit more complex than that. Evidence has shown that the business cycle exhibits the highest predictive power of one to three years.
Question
A situation in which actual output is below maximum potential output most likely reflects a:
- Budget deficit.
- Positive output gap.
- Negative output gap.
Solution
The correct answer is C.
Use the following formula:
$$ \text{Actual output} – \text{Maximum potential output} = {(+/-) \text{ Output gap}} $$
This formula states that when actual output exceeds maximum output, a positive output gap exists as the economy is outperforming, i.e., overheating. A negative output gap is the opposite. The actual output is below the maximum potential output.
A is incorrect. A budget deficit occurs when government expenses exceed revenue, and it is not directly related to the actual output of an economy being below its maximum potential output.
B is incorrect. A positive output gap occurs when actual output exceeds potential output, meaning growth is inflationary and above the trend rate. In contrast, a situation where actual output is below maximum potential output reflects a negative output gap, with an economic downturn with unemployment and spare capacity.
Reading 1: Capital Market Expectations – Part 1 (Framework and Macro Considerations)
Los 1 (f) Discuss how business cycles affect short- and long-term expectations
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.