Probability Tree and its Application t ...
A tree diagram is a visual representation of all possible future outcomes and... Read More
The sum of squares of a regression model is usually represented in the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) table. The ANOVA table contains the sum of squares (SST, SSE, and SSR), the degrees of freedom, the mean squares (MSR and MSE), and F-statistics.
The typical format of ANOVA is as shown below:
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c}
\textbf{Source} & \textbf{Sum of Squares} & \textbf{Degrees} & \textbf{Mean} & \textbf{F-statistic} \\
& & \textbf{of} & \textbf{square} & \\
& & \textbf{Freedom} & & \\ \hline
{ \text{Regression} \\ \text{(Explained)} } & SSR=\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(\widehat{Y_i}-\bar{Y}\right)^2 &
1 & MSR=\frac{SSR}{1} & F=\frac{MSR}{MSE} \\ \hline
{ \text{Residual} \\ \text{(explained)} } & SSE=\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(Y_i-\widehat{Y_i}\right)^2 & n-2 & MSE=\frac{SSE}{n-2} & \\ \hline
\text{Total} & SST=\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(Y_i-\bar{Y}\right)^2 & n-1 & &
\end{array} $$
Standard Error of EstimateStandard Error of Estimate, \(S_e\) or \(SEE\), is referred to as the root mean square error or standard error of the regression. It measures the distance between the observed and dependent variables predicted by the regression model. The Standard Error of Estimate is easily calculated from the ANOVA table using the following formula:
$${\text{Standard Error of Estimate }}(S_e)=\sqrt{MSE}=\sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i = 1}^{n}\left(Y_i-\hat{Y}\right)^2}{n-2}}$$
The standard error of estimate, coefficient of determination, and F-statistic are the measures that can be used to gauge the goodness of fit of a regression model. In other words, these measures are used to tell the extent to which a regression model syncs with data.
The smaller the Standard Error of Estimate is, the better the fit of the regression line. However, the Standard Error of Estimate does not tell us how well the independent variable explains the variation in the dependent variable.
Example: Calculating and Interpreting F-Statistic
The completed ANOVA table for the regression model of the inflation rate against the unemployment rate over 10 years is given below:
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c}
\textbf{Source} & \textbf{Sum of} & \textbf{Degrees of} & \textbf{Mean Sum} & \textbf{F-Statistic} \\
& \textbf{Squares} & \textbf{Freedom} & \textbf{of Squares} & \\ \hline
\text{Regression} & 10.568 & 1 & 10.568 & ? \\ \hline
\text{Error} & 3.136 & 8 & 0.392 \\ \hline
\text{Total} & 13.704 & 9
\end{array} $$
Solution
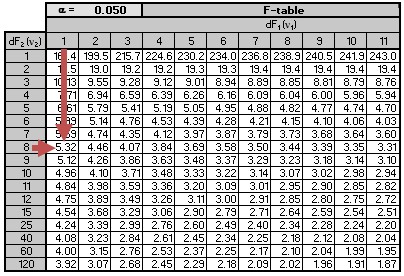 Remember that the null hypothesis is rejected if the calculated value of the F-statistic is greater than the critical value of F. Since \(26.960 \gt 5.32\), we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the slope coefficient is significantly different from zero. Notice that we also rejected the null hypothesis in the previous examples. We did so because the 95% confidence interval did not include zero.An F-test duplicates the t-test in regard to the slope coefficient significance for a linear regression model with one independent variable. In this case, \(t^2={2.306}^2\approx 5.32\). Since the F-statistic is the square of the t-statistic for the slope coefficient, its inferences are the same as the t-test. However, this is not the case for multiple regressions.
Remember that the null hypothesis is rejected if the calculated value of the F-statistic is greater than the critical value of F. Since \(26.960 \gt 5.32\), we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the slope coefficient is significantly different from zero. Notice that we also rejected the null hypothesis in the previous examples. We did so because the 95% confidence interval did not include zero.An F-test duplicates the t-test in regard to the slope coefficient significance for a linear regression model with one independent variable. In this case, \(t^2={2.306}^2\approx 5.32\). Since the F-statistic is the square of the t-statistic for the slope coefficient, its inferences are the same as the t-test. However, this is not the case for multiple regressions.Question
Consider the following analysis of variance (ANOVA) table:
$$
\begin{array}{c|c|c|c}
\textbf {Source} & \textbf {Degrees of} & \textbf { Sum of } & \textbf {Mean Sum} \\
& \textbf{Freedom} & \textbf {Squares} & \textbf{of Squares} \\ \hline
\text {Regression} & 1 & 1,701,563 & 1,701,563 \\ \hline
\text {Error} & 3 & 106,800 & 13,350 \\
\text {(Unexplained)} & & & \\ \hline
\text {Total} & 4 & 1,808,363 & \\
\end{array}
$$The value of \(R^2\) and the F-statistic for the test of fit of the regression model are closest to:
- 6% and 16.
- 94% and 127.
- 99% and 127.
Solution
The correct answer is B.
$$R^2=\frac{\text{Sum of Squares Regression (SSR)}}{\text{Sum of Squares Total (SST)}}=\frac{1,701,563}{1,808,363}=0.94=94\%$$
$$ \begin{align*} F & =\frac{\text{Mean Regression Sum of Squares (MSR)}}{\text{Mean Squared Error (MSE)}} \\ & =\frac{1,701,563}{13,350} =127.46\approx 127 \end{align*}$$
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.