Measures for Fixed-Rate Bonds and Floa ...
Yield Measures for Fixed-rate Bonds Fixed-rate bonds are those that pay the same... Read More
[vsw id=”7zXN8w_K6dQ” source=”youtube” width=”611″ height=”344″ autoplay=”no”]
A bond indenture is a legal document that outlines all the parameters of the bond issue, such as the par amount, issuer, coupon rate, security pledge, and the rights of bondholders. When analyzing a bond, it is important to review the credit risk of the issuer – the entity legally obliged to repay the bondholders. The indenture will also describe the security ranking of the bonds, which can be secured or unsecured. Secured bonds grant bondholders a claim on a specific asset, while unsecured or debentures offer no collateral and are repaid after secured bonds.
Collaterals are assets or guarantees that a lender accepts as security for a bond above and beyond the issuer’s promise to pay. Collateral backing serves to increase the credit quality of a bond and is one of the factors considered when determining the payable interest rate. In the event of a winding up, secured bonds or debts rank higher than unsecured debts.
Some of the items often used as collateral include physical equipment, mortgages, and stocks.
It’s important to identify the issuer of a bond by its legal name. The investor must understand who the issuer is. The issuer can be:
Covered bonds are securities issued by a bank or mortgage institution and collateralized against a pool of assets. Unlike asset-backed securities, covered bonds offer more protection to the bondholder since the pool of assets remains on the financial institution’s balance sheet. In the event of default, bondholders have recourse against both the cover pool and the financial institution.
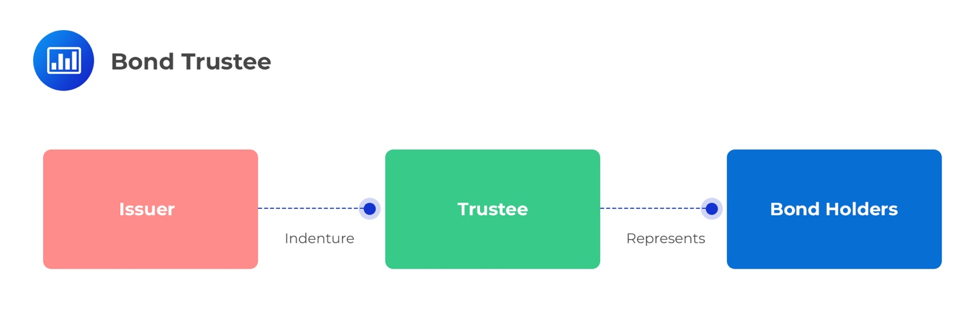
In certain situations, the bondholder may have difficulties determining whether the issuer is abiding by the outlined contractual obligations, also known as covenants. For instance, a stipulation could bar the issuer from issuing similar bonds for a specified period of time. For this reason, the bondholder may enlist the services of a trustee who acts in a fiduciary capacity for the them. The trustee is usually a third party with trust powers, such as the trust department of a bank. A summary of the trustee’s duties may include:
Other covenants that may be outlined in the indenture include actions such as:
Bonds can also have credit enhancements that improve the bonds’ credit quality and reduce the interest costs to the issuer. An internal credit enhancement ranges from distinguishing bonds based on the level of seniority compared to other debt obligations, providing more collateral than is needed for the bonds (over-collateralization), or establishing a reserve account that the issuer can use if they have insufficient funds to repay bondholders. An external credit enhancement is generally an insurance product that may take the form of a surety bond, letter of credit, or a cash collateral account.
Question
Samsung’s subordinate bonds offer no collateral. These bonds are most likely:
- Secured.
- Unsecured.
- Overcollateralized.
Solution
The correct answer is B.
Unsecured bonds offer no collateral and are repaid after secured bonds. Instead, the issuer promises that they will be repaid. This promise is frequently called “full faith and credit.”
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.