Credit Cycles
Credit cycles describe the changing availability and pricing of credit. They describe the... Read More
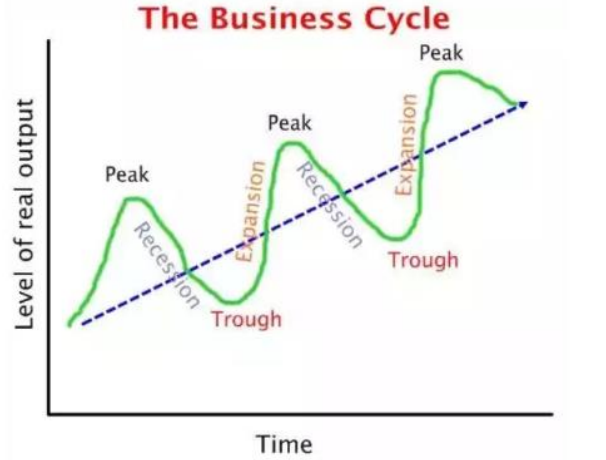
A business or economic cycle is defined as the persistent fluctuation in the gross domestic product of a given economy within a specified period. A business cycle can be described by periods of expansion and recessions.
During a recession, the economy contracts when measured by industrial production decrement, personal incomes, employment, and sales. Conversely, during an expansionary period, there is a significant growth in economic output. Business cycles are, therefore, measured by analyzing the fluctuations of the gross domestic product of an economy. Any given business cycle generally lasts between 1 to 12 years.
The growth of global economic activity defines expansion phases. Its features include economic growth, upward pressure on prices, and an increase in employment.
On a graph, the expansion comes after the trough, while contraction emerges after the peak and before the trough. During periods of expansion, a significant amount of the labor force is absorbed by the economic activities in the economy. This causes a reduction in the unemployment rate.
Peaks represent the highest value reached by some quantity in a certain period of time. For example, a peak is attained when the economy produces the highest output, inflation pressures prices to rise, and the unemployment rate is at its lowest.
Contractions happen when there’s negative economic growth or an economic decline. Prices decline, and the unemployment rate increases.
The trough is defined as the lowest point of business cycles. Here, the economy has hit rock bottom, out of which the next expansion phase will emerge. A good example of this is the 2008 financial crisis, where the unemployment rate was fairly high, and housing prices were at their lowest levels ever seen in years.
Question
Which of the following is most likely an indicator of an economy that is undergoing a recession?
- When the central bank starts buying back treasury securities.
- When the real GDP has two consecutive quarters of negative growth.
- When there is a huge decline of economic activities in the business sector.
Solution
The correct answer is C.
GDP measures the size of an economy. The most common technical indicator of a recession is two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth as measured by the GDP.
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.