Features and Characteristics of Infras ...
Infrastructure investments serve a societal role by promoting widespread economic, technological, and social... Read More
Methods of investing in alternative investments include:
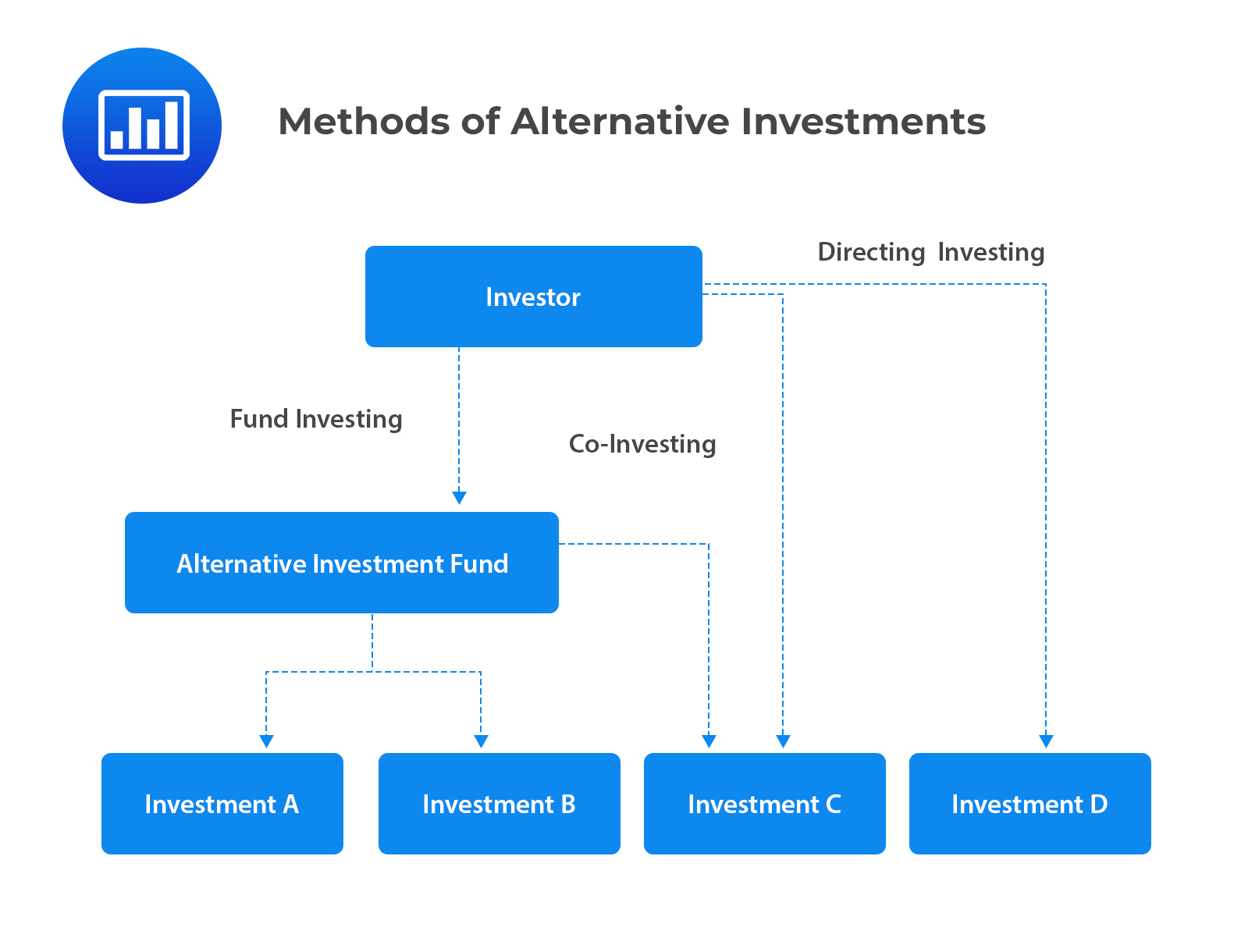
In fund investing, investors contribute capital to a fund, and then the fund identifies, chooses, and makes investments on behalf of the investors. Investors pay a fee based on the value of the fund managers’ assets. In addition, they pay a performance fee if the fund manager delivers a return above the benchmark.
Fund investing can be termed as indirect investing in alternative assets. This is because fund investors’ investment decisions are based on whether to invest in a fund or not. Furthermore, investors do not influence a fund’s investments.
Fund investing applies to all types of alternative investments.
In co-investing, an investor indirectly invests in assets through a fund. Nevertheless, the investor owns the rights (co-investment rights) to invest in the same assets directly. Intuitively, co-investing allows the investor to make parallel investments when the fund identifies a lucrative deal.
In direct investment, an investor directly invests in an asset without using any intermediary. Direct investing, therefore, gives investors higher control and flexibility when selecting investments, financing methods, and approaches. However, investing directly in alternative investments is most popular among established private equity and real estate investors. Pension funds and sovereign wealth funds may also invest in infrastructure and natural resources.
In direct investment, an investor chooses the company to invest in. However, there is a need for high and competence-based due diligence before they invest in a private company.
Fund investing provides the benefits of a diversified portfolio, but this advantage comes at an additional cost. Even though the fund performs due diligence on the ventures to invest in, the investor, too, must perform due diligence on the fund manager, before investing in a fund.
In co-investing, the general partner assists the investor in performing direct due diligence on a portfolio company.
Question
Which of the following is most likely a disadvantage of co-investing?
A. It may be subject to adverse selection bias.
B. The investor won’t enjoy fund diversification benefits.
C. Selecting the right fund is not easy because of the information asymmetry.
Solution
The correct answer is A.
Co-investing may be subject to adverse selection bias. This is because the fund avails less attractive investment opportunities to the co-investor while allocating its own capital to more appealing deals.
B is incorrect. Being unable to enjoy the diversification benefits is a disadvantage of direct investing, not co-investing.
C is incorrect. Selecting the right fund is difficult because information asymmetry is a disadvantage of fund investing.