Introduction to Probability: Definitio ...
Probability is a measure of the likelihood that something will happen. We usually... Read More
A cumulative distribution function, \(F(x)\), gives the probability that the random variable \(X\) is less than or equal to \(x\):
$$ P(X ≤ x) $$
By analogy, this concept is very similar to the cumulative relative frequency.
A cumulative distribution is the sum of the probabilities of all values qualifying as “less than or equal” to the specified value. Perhaps an example will make this concept clearer.
If we flipped a coin three times, we would end up with the following probability distribution of the number of heads obtained:
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c} \textbf{Heads (outcomes)} & \bf{0} & \bf{1} & \bf{2} & \bf{3} \\ \hline \text{Probability} & {1/8} & {3/8} & {3/8} & {1/8} \\ \end{array} $$
To come up with a cumulative distribution function, we have to calculate the cumulative probabilities:
The cumulative probability that \(X\) is less than or equal to zero is 1/8.
To find the cumulative probability that \(X\) is less than or equal to 1, we add \(P(X = 0)\) and \((P = 1)\):
$$ P(X \le 1) =\cfrac {1}{8} + \cfrac {3}{8} = \cfrac {1}{2} $$
Similarly,
$$ P(X \le 2) = \cfrac {1}{8} + \cfrac {3}{8} + \cfrac {3}{8} = \cfrac {7}{8} $$
Lastly,
$$ P(X \le 3) = \cfrac {1}{8} + \cfrac {3}{8} + \cfrac {3}{8} +\cfrac {1}{8} = 1 $$
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c} \textbf{Heads (outcomes)} & \bf{0} & \bf{1} & \bf{2} & \bf{3} \\ \hline \text{Probability} & {1/8} & {3/8} & {3/8} & {1/8} \\ \hline \text{Cumulative prob.} & {1/8} & {4/8} & {7/8} & {8/8} \\ \end{array} $$
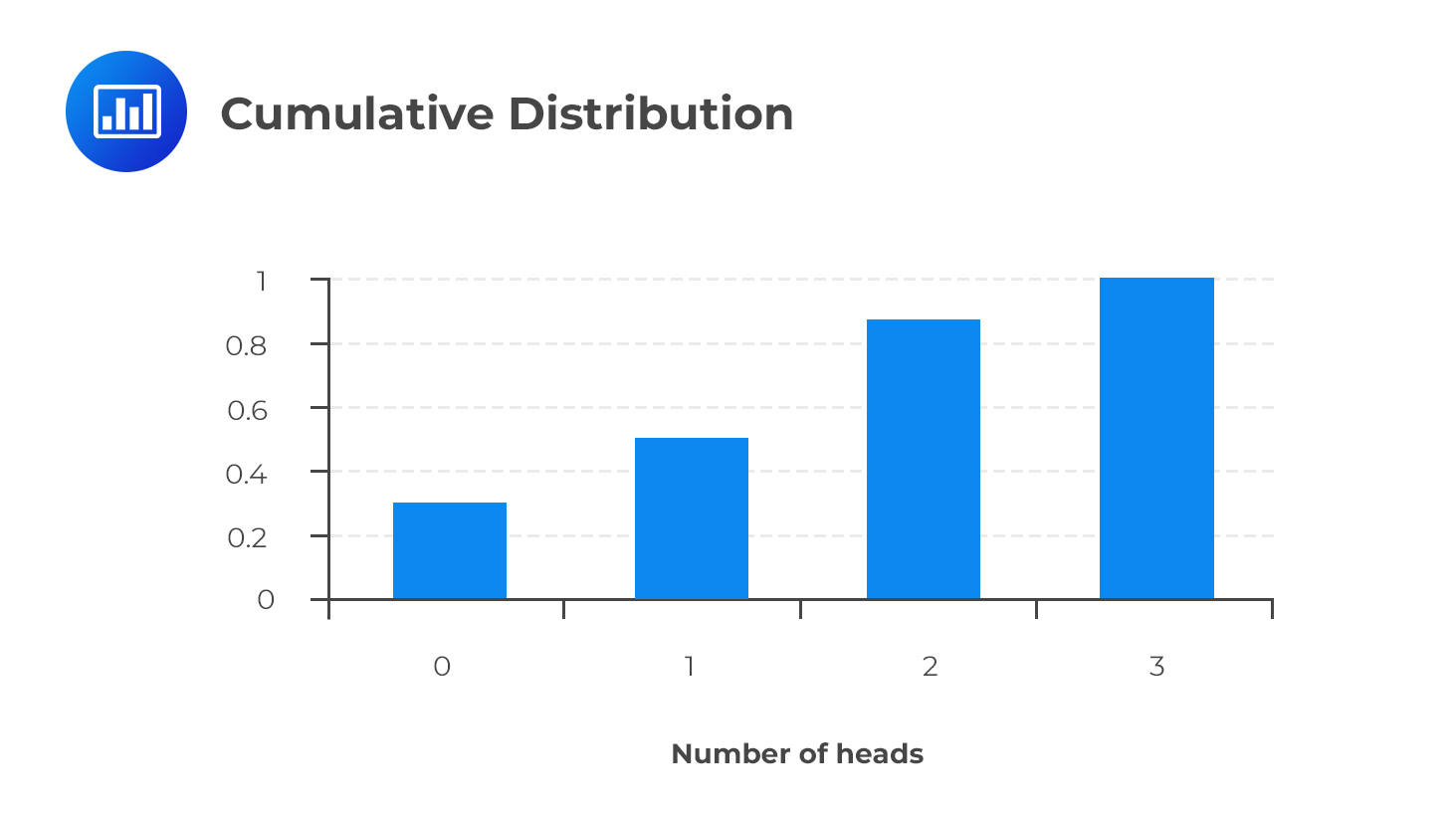
The CDF has two main properties:
A cumulative distribution function can help us to come up with cumulative probabilities pretty easily. For example, we can use it to determine the probability of getting at least two heads, at most two heads, or even more than two heads. The probability of at most two heads from the cumulative distribution above is 0.875.
Variable X can take values 1, 2, 3, and 4. The probability of each outcome has been given below.
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c} \textbf{Outcome} & \bf{1} & \bf{2} & \bf{3} & \bf{4} \\ \hline \text{Probability} & {0.2} & {0.3} & {0.35} & {0.15} \\ \end{array} $$
Determine \(P(X ≤ 2)\).
A. 0.5.
B. 0.3.
C. 0.85.
Solution
The correct answer is A.
You simply sum up the probabilities up to and including a given outcome and come up with a table similar to the one below:
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c} \textbf{Heads (outcomes)} & \bf{1} & \bf{2} &\bf {3} & \bf{4} \\ \hline \text{Probability} & {0.2} & {0.3} & {0.35} & {0.15} \\ \hline \text{Cumulative prob.} & {0.2} & {0.5} & {0.85} & {1} \\ \end{array} $$
From the table, it is clear that \(P(X \le 2) = 0.5\).
Note to candidates: The standard notation for a cumulative distribution function is written in upper case \(F(x)\). In contrast, that of a probability function is written in lowercase \(f(x)\).
A cumulative distribution offers a convenient tool for determining probabilities for a given random variable. As seen above, the cumulative distribution function, \(F(x)\), gives the probability that the random variable \(X\) is less than or equal to \(x\) for every \(x\) value. It is usually expressed as:
$$ F(x) = P(X \le x) $$
The random variable X has the following probability distribution function:
$$ \begin{matrix} P(x) = \frac { x }{ 150 } & \text{ for x} = 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{matrix} $$
Calculate and interpret \(F(20)\) and \(F(40)\).
Solution
As you will recall, we can determine the probability of each outcome for a random variable given the probability distribution function (pdf).
$$ \begin{align*} P(x) & =\cfrac {x}{150} \\ P(x) & = P(X = x) \\ \end{align*} $$
Therefore,
$$ P(10) =\cfrac {10}{150} $$
Similarly,
$$\begin{align} P(20) &=\cfrac {20}{150} \\ P(30) &=\cfrac {30}{150}\\ P(40) &=\cfrac {40}{150}\end{align}$$
And lastly,
$$ P(50) =\cfrac {50}{150} $$
Note to candidates: We can prove that our pdf is correct by testing the first rule of probability distribution functions by adding all the probabilities.
Now,
$$ F(x) = P(X \le x) $$
Therefore,
$$ \begin{align*} F(2) & = P(X \le 20) \\ & = P(X = 10) + P(X = 30) \\ & =\cfrac {10}{150} + \cfrac {20}{150} \\ &=\cfrac {30}{150} \text { or } \cfrac {1}{5} \\ \end{align*} $$
Interpretation: There is a 20% cumulative probability that outcomes 10 or 20 occur.
Similarly,
$$ \begin{align*} F(40) & = P(X \le 40) \\ & = P(X = 10) + P(X = 20) + P(X = 30) + P(X = 40) \\ & =\cfrac {10}{150} + \cfrac {20}{150} + \cfrac {30}{150} + \cfrac {40}{150} \\ & = \cfrac {100}{150} \text{ or } 66.67\% \\ \end{align*} $$
Interpretation: There is a 66.67% cumulative probability that outcomes 10, 20, 30, or 40 occur.
Variable \(X\) can take the values 1, 2, 3, and 4. The cumulative probability distribution is given below. Use it to calculate:
(a) P(X = 2).
(b) P(X = 4).
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c} \textbf{Outcome} & \bf{1} & \bf{2} & \bf{3} & \bf{4} \\ \hline \text{Cumulative Probability Distribution} & {0.2} & {0.5} & {0.85} & {1} \\ \end{array} $$
Solution
$$ F(x) = P(X \le x) $$
(a)
$$ \begin{align*} F(2) & = P(X \le 2) = 0.5 \\ 0.5 & = P(X = 1) + P(X = 2) \\ & = 0.2 + P(X = 2)\\ P(X = 2)& = 0.5 – 0.2 = 0.3 \\ \end{align*} $$
Note to candidates: A simpler, more direct approach can be:
$$ P(X = 2) = F(2) – F(3) $$
Therefore,
$$ P(X = 2) = 0.5 – 0.2 = 0.3 $$
(b)
$$ \begin{align*} P(X = 4) & = F(4) – F(3) \\ &= 1 – 0.85 = 0.15 \\ \end{align*} $$
Question
Given the following cumulative probability distribution, determine \(P(X=2)\).
$$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c} \textbf{Outcome} & \bf{0} & \bf{1} & \bf{2} & \bf{3} \\ \hline \text{Cumulative prob.} & {1/8} & {4/8} & {7/8} & {1} \\ \end{array} $$
- \(\frac{7}{8}\).
- \(\frac{3}{8}\).
- \(\frac{1}{8}\).
Solution
The correct answer is B.
$$ \begin{align*} P(X = 2)& = F(2) – F(1) \\ &=\cfrac {7}{8} – \cfrac {4}{8} \\ & =\cfrac {3}{8} \\ \end{align*} $$
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.