CFA® Exam Preparation Survey
Keeping true to our commitment to nourishing CFA exam candidates with relevant career... Read More
Understanding call and put option payoffs is a must for mastering derivatives in the CFA® or FRM® exams—and for real-world trading strategies. This guide breaks down option payoff and profit formulas, shows you how to calculate each, and includes charts to visualize your risk and return. Whether you’re a candidate or a curious investor, this is the only reference you need to get it right.
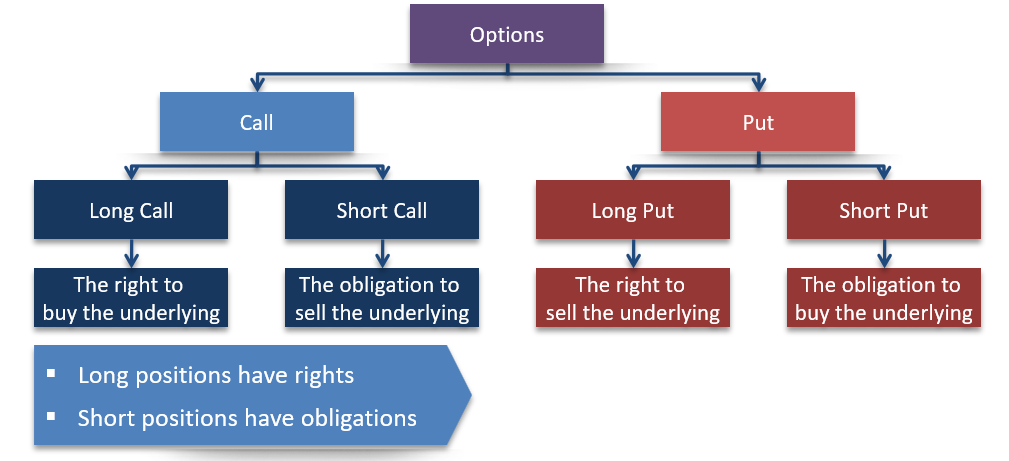
The buyer of an option has the right but not the obligation to exercise the option. The maximum loss to the buyer is equal to the premium paid for the option. The potential gains are theoretically infinite. To the seller (writer), however, the maximum gain is limited to the premium received after writing the option. The potential loss is unlimited.
In an options contract, two parties transact simultaneously. The buyer of a call or a put option is the long position in the contract while the seller of the option, also known as the writer of the option, is the short position.
The payoff for a call buyer at expiration date T is given by \(max(0,S_T–X)\) while the payoff for a call seller is \(-max(0,S_T–X)\).
Where:
\(S_T\) is the price of the underlying at expiration; and
X is the exercise price.
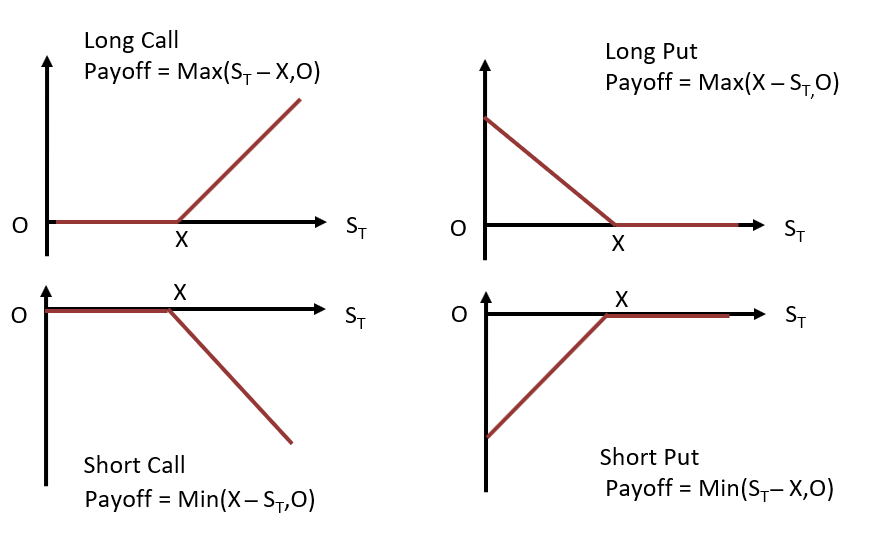
Using the payoff profile and the price paid for the option, the profit equation of a call option can be written as follows:
Payoff for a call buyer \(=max(0, S_T-X)\)
Profit for a call buyer \(=max(0, S_T–X)-c_0\)
Payoff for a put seller \(=-max(0,S_T–X)\)
Profit for a call seller \(=-max(0, S_T–X)+c_0\)
where \(c_0\) the call premium.
The buyer of the call option has no upper limit on the potential profit and a fixed downside loss equal to the premium. The seller, on the other hand, has unlimited losses and a gain limited to the premium:
The profit from buying one European call option: Option price = $10, Strike price = $200 can be shown as follows:
The profit from writing one European call option: Option price = $10, Strike price = $200 is shown below:
By now, if you have well understood the basic characteristics of call options, then the payoff and profit for put option buyers and sellers should be quite easy; simply replace \( “S_T-X” \text{ by } “X-S_T” \).
https://analystprep.com/shop/cfa-unlimited-package-for-level-1-2-3/
The payoff and profit profiles of a put option are represented as follows:
Payoff for a put buyer \(=max(0,X-S_T)\)
Profit for a put buyer \(=max(0,X-S_T)-p_0\)
Payoff for a put seller \(=-max(0,X-S_T)\)
Profit for a put seller \(=-max(0,X-S_T)+p_0\)
Where \(p_0\) is the put premium.
The put buyer has a limited loss and, while not completely unlimited gains, as the price of the underlying cannot fall below zero, the put buyer does gain as the price falls. As such, purchasing a put option is like purchasing insurance. In the same vein as for call options, the put seller has nearly unlimited losses, and his gains are limited to the put premium paid to him by the put buyer.
The profit from buying a European put option: Option price = $14, Strike price = $140.
The profit from writing a European put option: Option price = $14, Strike price = $140.
At expiration, the underlying asset price \( S_T\) is $29. If the strike price X is $26, what is the payoff to the put and call buyers?
Solution
The payoff to the call buyer:
\(c_T=\ max(0,S_T\ – X) = max(0,$29 – $26) = $3\)
The payoff to the put buyer:
\(p_T=\ max(0,X\ – S_T) = max(0,$26 – $29) = 0\)
When the option has a positive payoff, it is said to be in the money. In the example above, the call option is in the money. The put option is out of the money because \(X\ – S_T\) is less than 0. When \(S_T\ =\ X\), the option is said to be at the money.
Assume that a put and call on XYZ stock have the same strike price of X = $35. The call initially costs $2, and the put costs $3.
What is the profit on the long call and long put if the price of CBX stock at expiration \(S_T\) is $28?
Solution
Profit to the call buyer \(=max(0,S_T–X)-c_0=max(0,$28 – $35) – $2 = – $2 \)
Profit to the put buyer \(=\ max(0,X\ – S_T) – p_0 = max(0,$35 – $28) – $3 = $4\)
Exchange-traded stock options can either be American or European style. While European options can only be exercised at expiry, American options can be exercised at any point during the life of the option. The exchange specifies the actual date of expiry.
Тhe value of the stock directly controls the strike price. At the expiration date, the difference between the stock’s market price and the option’s strike price determines the payoff.
Call Options:
Put Options:
A stock has a current price of $100. The exercise price of a call option is $105.
Is the option in-the-money, at the money, or out of the money?
Solution
The call option is out of the money (OTM) since the stock price is less than the exercise price. The option would be in the money anywhere above the exercise price of $105.
A stock has a current price of $50. The exercise price of a put option is $45.
Is the option in-the-money, at the money, or out of the money?
Solution
The put option is out of the money (OTM) since the stock price exceeds the exercise price. The option would be in the money anywhere below the exercise price of $45.
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the prevailing market price of the underlying security and the strike price.
Call option
The intrinsic value of a call option is the \(max(0,\ S_T-\ X)\).
Put option
The intrinsic value of a put option is the \( max(0,\ X\ -S_T)\).
The time value of an option is the difference between the option premium and the intrinsic value.
\(Option\ premium\ =\ Intrinsic\ value+\ Time\ value\)
Consider a put option with a premium of $11, and the exercise price is $129. The price of the underlying security is $123. What are the value at expiration and the gain/loss to that put option buyer?
Solution
The exercise price is greater than the underlying price, i.e., $123 > $129.
Therefore the payoff \(p_T=0\) and \(profit=0-11=-11\).
Value at expiration = $0
Loss to the put buyer = $11
Practice real exam-style questions on options payoff and profit calculations to sharpen your skills and boost your confidence.
Try CFA Level 1 Practice Questions NowKeeping true to our commitment to nourishing CFA exam candidates with relevant career... Read More
You may have heard that it is challenging to pass the FRM exam,... Read More