Measures for Fixed-Rate Bonds and Floa ...
Yield Measures for Fixed-rate Bonds Fixed-rate bonds are those that pay the same... Read More
A hypothetical financial institution, BCG Bank, decides to raise a $100 million loan by securitizing loans rather than issuing corporate bonds. The company sets up a legal entity, Loan Trust, to which it sells the loans. Such a legal entity is called a Special Purpose Entity (SPE) or Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV).
The ultimate owner of the loan, Loan Trust, is not, in any way, is considered bankruptcy-free from the seller of the loans. The loans backed by asset-backed securities are accepted to be safe within the SPE, and creditors of BCG don’t have any claims on these assets.
BCG sells $100 million of loans and receives $100 million in cash. In turn, Loan Trust issues and sells securities that are backed by securitized loans (represents collateral) and receives cash. Periodic cash payments that are received from the collateral, for instance, monthly mortgage payments made by borrowers, are used to make periodic cash payments to security holders, i.e., the investors who bought the asset-based securities. These investors are often large pension funds.
In our foregoing example, the money flows in the following manner:
In addition, the following are the other parties involved in the securitization process: independent accountants, lawyers, trustees, underwriters, rating agencies, financial guarantors, liquidity support, etc.
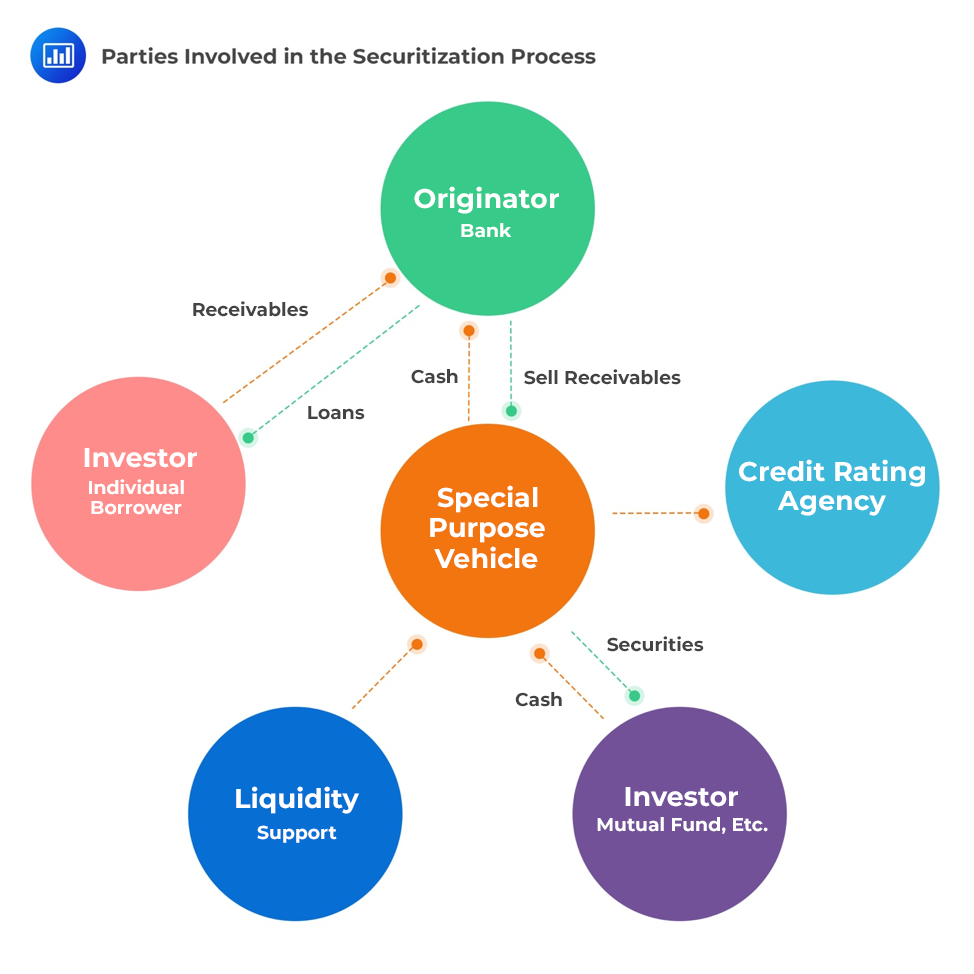
A significant amount of legal documentation is required to create a special purpose entity. The purchase agreement is signed by the seller of the collateral and the SPE. Another important legal document is the prospectus which describes the structure of securitization, such as the priority of payments to be made to parties.
Question
Which of the following parties is likely to be referred to as the originator in the securitization process?
- Rogers Mutual Fund.
- Grand American Bank.
- Jim Blank, an individual mortgage borrower.
Solution
The correct answer is B.
The originator of the loan is usually a financial institution providing mortgage loans to individual borrowers. However, it is important to note that the securitization process does not always have to be based on mortgage loans.
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.