Explain LIFO Reserve and LIFO Liquidat ...
US GAAP requires companies that use the LIFO method to disclose the amount... Read More
The Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting (2010) provides important information on the concepts which underlie the preparation and presentation of financial statements. This framework is of great benefit to all financial statement users. It has several components that are outlined in figure 1 below.
Figure 1 – IFRS Framework for the Preparation and Presentation of Financial Reports
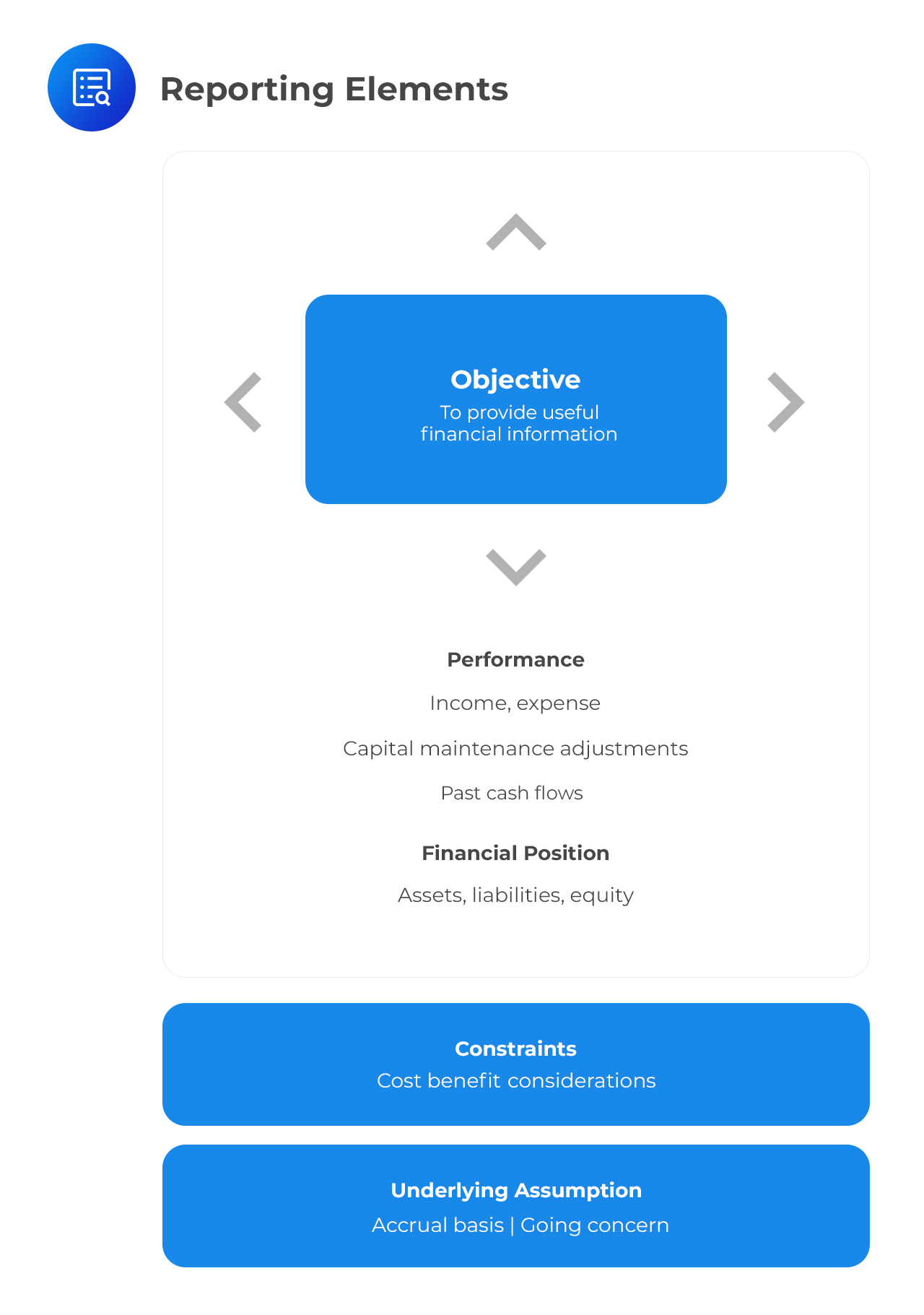
The Conceptual Framework (2010) has a core objective from which all its other aspects flow. This central objective is “to provide financial information which is useful to both current and potential providers of resources (investors, lenders, other creditors) in decision-making.“
The financial information to be provided will include: (i) information on a company’s financial position (its resources and financial obligations); (ii) information on a company’s financial performance (information which explains why the company’s financial position changed in the past); and (iii) information on the company’s cash and cash equivalents.
The Conceptual Framework (2010) identifies relevance and faithful representation as the two fundamental qualitative characteristics which make financial information useful. Financial information is relevant if it would potentially affect or make a difference in its consumer’s decision. Faithful representation relates to the fact that information that represents an economic phenomenon should ideally be complete, neutral, and free from error.
The Conceptual Framework (2010) also identifies comparability, verifiability, timeliness, and understandability as the four enhancing qualitative characteristics of information:
The cost of providing and using financial information is a constraint that must be balanced with the benefits that are to be derived from the information.
The financial effects of transactions and other events are represented in financial statements by grouping them into broad classes or elements. The grouping is done according to their economic characteristics.
The elements of financial statements that are directly related to financial positions are assets, liabilities, and equity. The elements directly related to financial performance, on the other hand, are income and expenses.
Accrual accounting and ‘going concern’ are two key assumptions that underlie the preparation of financial statements. These assumptions determine how financial statement elements are recognized and measured. Accrual accounting means that financial statements reflect transactions in the period in which they occur and not necessarily when cash movement occurs. ‘Going concern’ means that a company is assumed to continue in business for the foreseeable future.
Recognition refers to the inclusion of an item on the balance sheet or income statement. An item should be recognized if it is probable that future economic benefits that are associated with it will flow to or from the reporting entity, and it has a cost or value that can be reliably measured.
In measuring financial statement elements, the following bases of measurement may be used:
Question
According to the Conceptual Framework (2010), which of the following are the two fundamental qualitative characteristics that make financial information useful?
- Timeliness and understandability.
- Relevance and faithful representation.
- Accrual accounting and going concern.
Solution
The correct answer is B.
The Conceptual Framework (2010) identifies relevance and faithful representation as the two fundamental qualitative characteristics which make financial information useful.
‘Timeliness’ and ‘understandability’ are two of the enhancing qualitative characteristics of information, while ‘accrual accounting’ and ‘going concern’ are the underlying assumptions identified by the Conceptual Framework (2010).
Get Ahead on Your Study Prep This Cyber Monday! Save 35% on all CFA® and FRM® Unlimited Packages. Use code CYBERMONDAY at checkout. Offer ends Dec 1st.