Hedge Fund Fees
Management and Incentive Fees Hedge fund fees are usually two-fold: management fees and... Read More
Commodities and raw land are the two main categories of natural resources for investment purposes.
Commodities are tangible goods that can be standardized in quality, location, and delivery in the process of investing. Commodities may be classified as hard or soft commodities. Hard commodities are mined or extracted. Examples of such commodities are oil, copper, and gold. On the other hand, soft commodities are bred or grown for many years. Examples of soft commodities are livestock and cash crops, among many others.
Commodities can also be classified by physical location and quality, which must be specified in derivative contracts. For example, there are different grades of crude oil.
Price fluctuations generally determine commodity investment returns as opposed to income. Holding commodities occasions incurrence of transportation and storage costs. Therefore, investors prefer to trade commodity derivatives.
The commodity derivative index price volatility is significantly connected to the price volatility of the underlying physical items.
Supply chain participants use futures to hedge their physical commodity purchases and sales. The basis for most commodity investments is futures, where each contract is for future delivery or receipt of a specified quantity of a commodity. The future price is derived from:
$$\text{Future price} \cong \text{Spot price} \left(1+r\right)+\text{Strorage costs-Convenience yield}$$
Where:
\(r\) = The period’s short-term risk-free interest rate.
The total of storage and interest costs is referred to as the cost of carry or the carry.
Since buyers of futures contracts cannot access the products and benefit from them, future prices are adjusted for the loss of this convenience using the convenience yield. Future prices differ from the spot prices depending on the convenience yield.
When future prices are higher than spot prices, the prices are said to be in contango, and the commodity forward curve slopes upwards. This happens when there is little or no convenience yield. Prices are said to be in backwardation when futures prices are lower than spot prices, resulting in a commodity forward curve that is downward sloping. This happens when the convenience yield is high.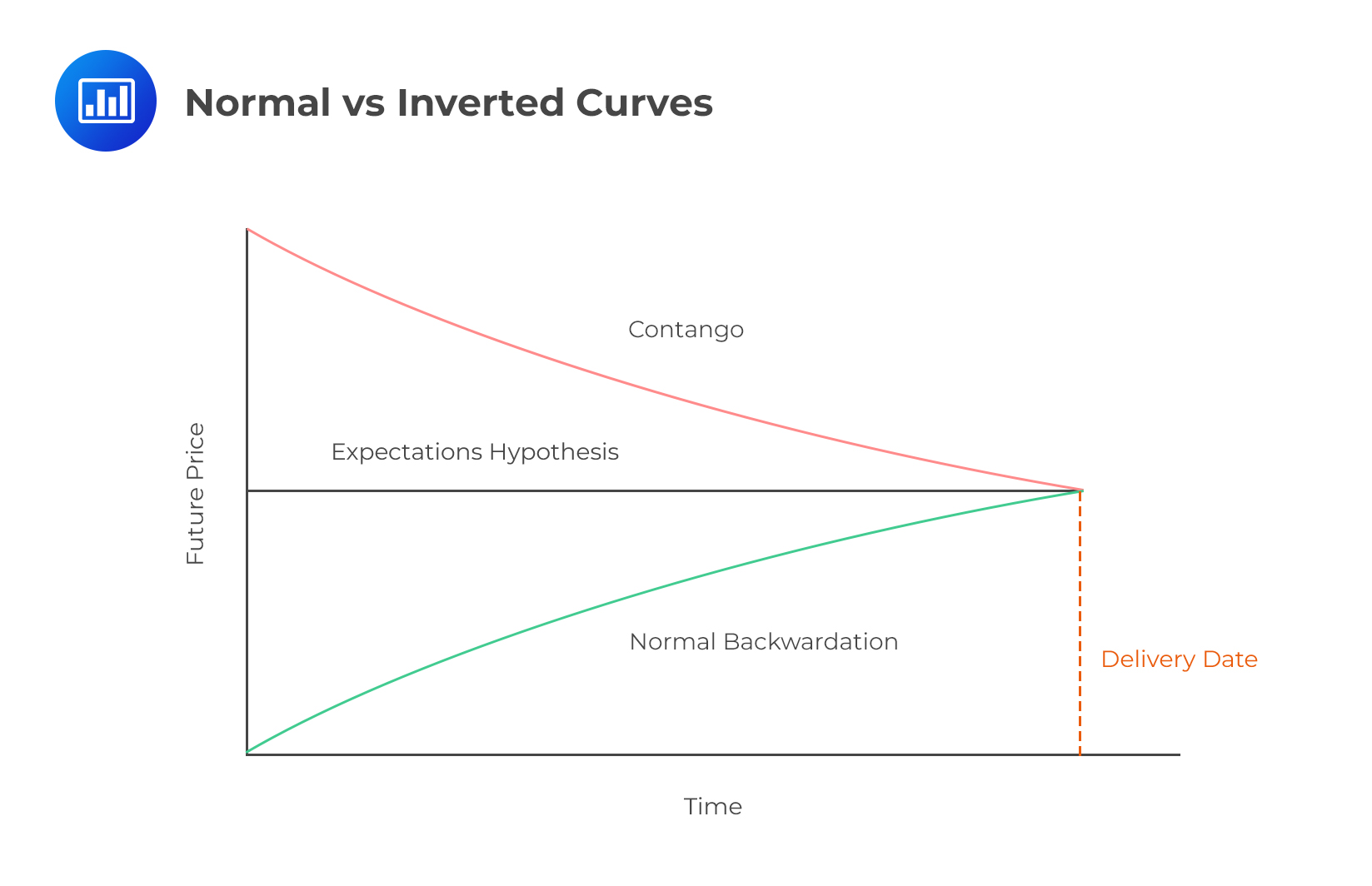
Cryptocurrency is considered a digital currency or digital commodity, or asset. It is recognized and regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
A digital asset may be defined as anything that can be stored and transmitted electronically and has associated use rights.
Key Features
The term “digital asset” is more general and covers a wider range of uses, such as ownership, transaction tracking, identity management, and smart contracts. The properties of a commodity or commodity derivative may be expressed in a digital asset.
A digital token is a digital asset that can be used for more than just virtual currency and operates on another blockchain network.
Virtual currencies, also called coins or tokens, are intended to serve as a medium of exchange.
Investment in commodities can be made through derivatives such as futures, swaps, forwards, and options. Although physical commodities can be traded, such a trade is often characterized by price obscurity, tax issues, and huge costs.
Apart from physical commodity investment and use of derivatives, achievement of commodity exposure can be done through the following:
Raw land is utilized for farming and/or growing timber. Examples of raw lands include timberland and farmland.
A real estate property title represents ownership. A title deed spells out land use rights. The characteristics of farmland and timberland include:
The logic behind investment in commodities includes the possibility of returns, portfolio diversification, and inflation protection. That is, investors’ interest in commodities is inspired by the belief that prices will increase in short to intermediate periods. Moreover, since commodities directly influence the inflation index, they are appropriate for hedging against inflation risk, even when the return is minimal or there is no real return.
Production cannot be adjusted immediately. Producers require some time to adjust to demand. Investors will, therefore, seek to anticipate changes by closely monitoring economic conditions.
The demand for commodities is affected by global manufacturing fluctuations and economic growth. As such, investors in commodities need to be keen on their inventories and economic conditions, such as government policies and growth estimations.
Farmland and timberland provide low liquidity and a high risk of negative cash flow since fixed costs are relatively high, and revenue depends on the weather conditions. As such, weather is a unique risk for timberlands and farmland compared to real estate.
An additional primary risk in farmland and timberland is the international competitive landscape risk. Note that productive lands create commodities that are traded and consumed globally. As such, events such as interruptions of world trade and increasing agricultural competition may lead to lower commodity prices.
Apart from seeking profit, investors’ interest in natural resources is anchored upon the following factors:
Commodities are effective hedges against inflation. Their prices have historically been positively correlated with inflation.
Moreover, commodities are effective for portfolio diversification. Returns have had a low correlation with returns on other investments.
Investors can comply with ESG principles of responsible and sustainable investing by including timberland and farmland in their portfolios.
Timberland and farmland investments can take the form of public or private investment funds. Examples of public investment funds are real estate investment trusts (REITs) in the US. Private investment funds may include limited partnerships. Through investment funds, investors can own land in a foreign country in which they can plant different crops.
Question
Which of the following is most likely an effect of little or no convenience yield on prices?
- Backwardation.
- Contango.
- Convenience yield.
Solution
The correct answer is B.
Contango is when futures prices are higher compared to spot prices. This occurs when there is little or no convenience yield.
A is incorrect. Backwardation is when futures prices are lower than spot prices. This happens when the convenience yield is high.
C is incorrect. Convenience yield is the benefit or premium associated with holding an underlying product or physical good rather than the associated derivative security or contract.